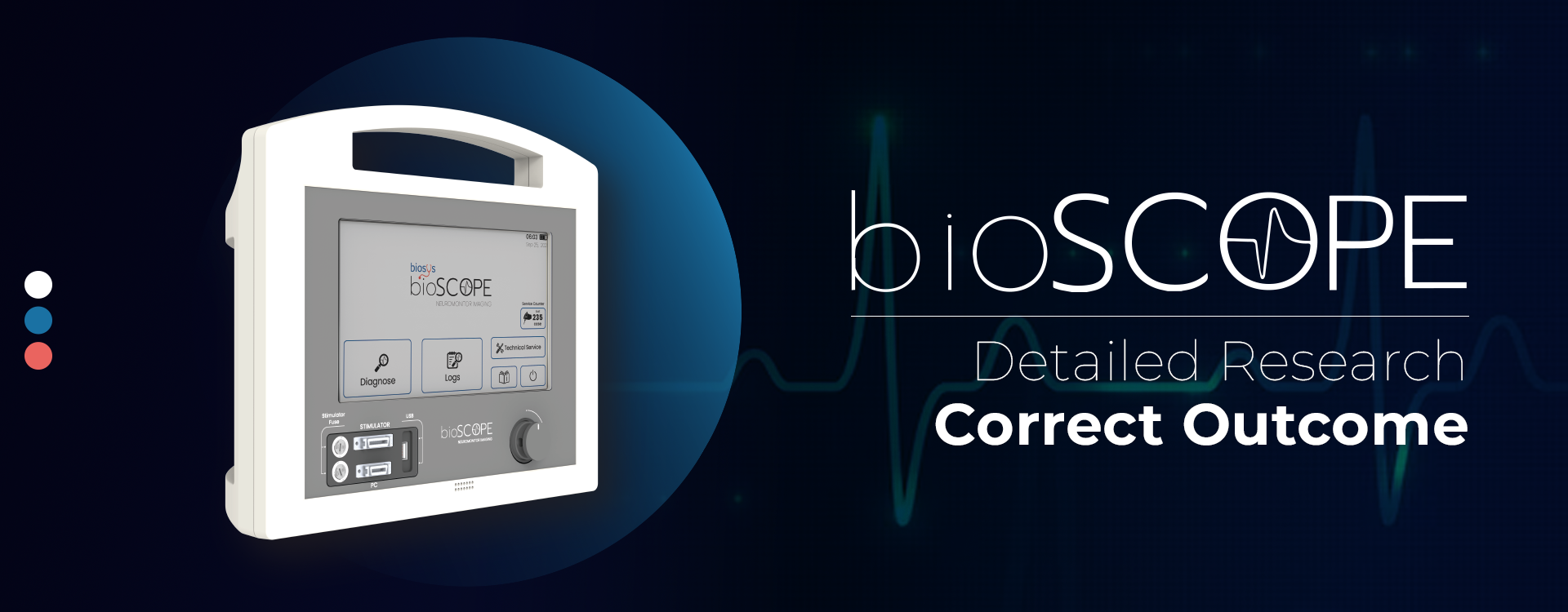
BIOSCOPE
Intraoperative Neuromonitor Device
Maximum Safety Against the Risk of Damage
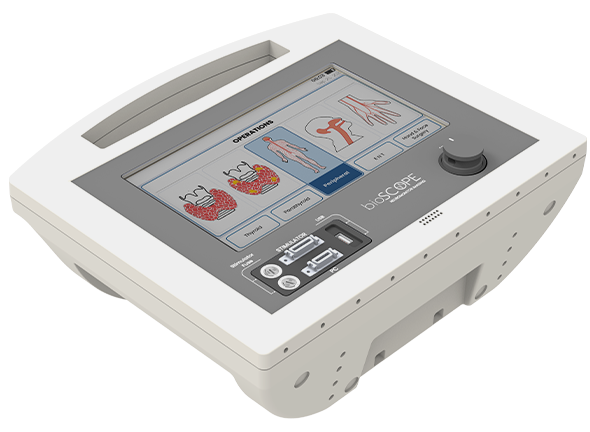
Bioscope intraoperative neuromonitor is essential for eliminating or minimizing the neurologic damages. Neuro-monitorization enables to assess the functional integrity of the neural structures under the risk of damage. It is a system that helps the surgeon for the purpose of protecting the patient health by monitoring visually and aurally the nerves under risk during bioscope thyroid, parathyroid, hand and face surgery.


2 Channel Signal Measurement and Sleep Mode
Bioscope has the most advanced signal measurement technology in its class, providing a top of the line experience. It also features an optional sleep mode for increased convenience.

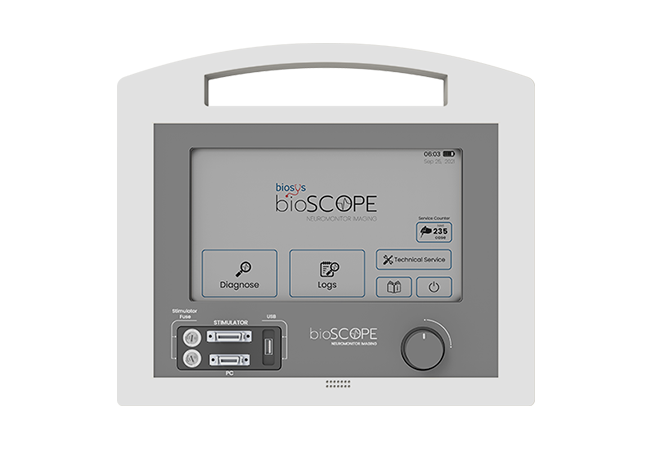
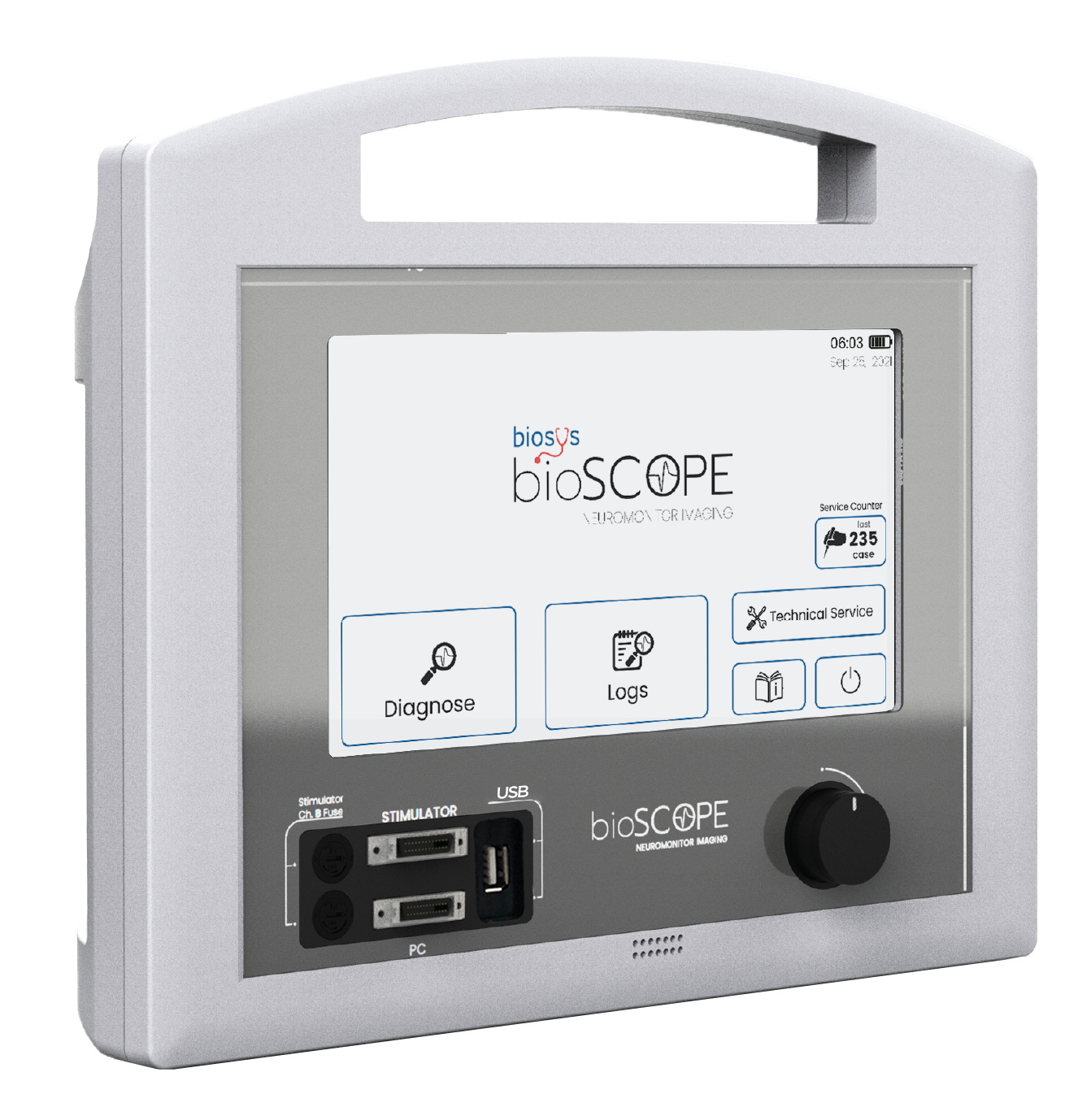
High Resolution Touch Screen
The advanced 10.1 inch touchscreen of Bioscope provides high-resolution imaging with easy-to-use options.
Applicable and Functional
Graphic Display
You can easily make precise flow adjustments during high-flow oxygen therapy.

Integrated Battery
Dual built-in battery system prevents interruption in operations due to power outages, during intraoperative neuromonitoring procedures, enabling up to 2 hour operation time.


Advanced Technology in Intraoperative Neuromonitor: Bioscope
Bioscope intraoperative neuromonitor device provides a monitoring purpose that notifies the anesthesia specialist and operating neurologist of an approaching injury so that they can adjust the course of treatment in time to avoid irreversible harm.
How Does Bioscope Intraoperative Neuromonitor Work?
- Electrodes are used for direct contact with the laryngeal nerve and surrounding tissues.
- Electric stimulation is created with the used electrode.
- The resulting electric stimulation is transmitted to the throat by the recurrent laryngeal nerve.
- The recording electrode converts the electric signal into sound and image, and the signals are controlled by the surgeon.
- If a waveform is seen on the monitor, it becomes apparent that recurrent laryngeal nerves that need to be carefully separated are nearby.

Comparison Chart
The table below shows the comparison between the Bioscope (Intraoperative Neuromonitoring Device) and a neuromonitor from another brand. The table is prepared to help you make your decision more easily.
 | A | |
|---|---|---|
| Protection Class / Type for Electricity | Class I, BF | Class I, BF |
| Supply Voltage | 100-240V | 100 V, 120 V / 230 V |
| Weight | 4.5 kg | 6.8 kg |
| Stimulus Range | 0.01-30 mA | 0-30 mA |
| Battery | 2 Hours | 5 Minute |
| Electrode Connection Check |  |  |
| PDF Reporting Function |  |  |
| IP Class (International Protection) | IP21 | IPX1 |
Enquire about the BIOSCOPE Intraoperative Neuromonitor Device
If you have an enquiry about our products, please provide the following information so a Biosys representative can contact you.
